Deploy Magda to Microsoft Azure
1> Install the Azure CLI
If you haven’t, follow the link below to install the Azure CLI.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli
2> In Azure Portal, create a Resource Group with a name you preferred. e.g. magda-deploy-res-group.
A
Resource Groupis a container that holds related resources for an Azure solution.
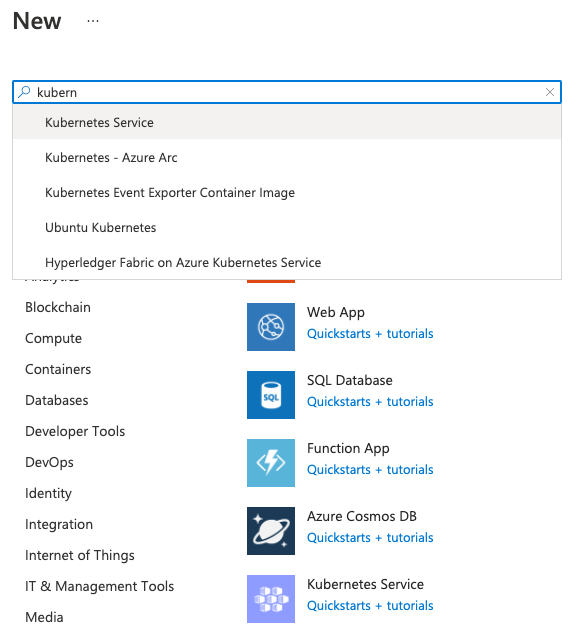
3> Go the resource group created, click “Add” button to add “Kubernetes Service”. If it is not already on the screen, you can find it from search input by key in “Kubernetes Service”. See screenshot below:
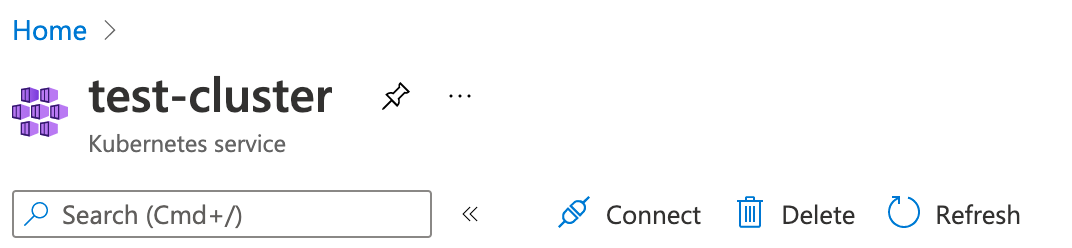
4> Open the “Kubernetes Service” resource that is just created (see screenshot below).
And click the “Connect” button to get the commands required to connect to your cluster and setup the k8s config for your local kubectl tool.
5> Install kubernetes-replicator
It’s only required by the OpenFaas part of Magda which can be turned off via global.openfaas.enabled.
# add helm chart repo
helm repo add mittwald https://helm.mittwald.de
# update helm chart repo
helm repo update
# create namespace `kubernetes-replicator`
kubectl create namespace kubernetes-replicator
# Install kubernetes-replicator via helm
helm upgrade --namespace kubernetes-replicator --install kubernetes-replicator mittwald/kubernetes-replicator
6> Create a namespace “magda” for your Magda installation
kubectl create namespace magda
7> Create required secrets
You need pwgen command line tool to follow the instruction below. If it’s not availble on nyour system, you need to install one.
export JWT_SECRET="$(pwgen 32 1)"
export SESSION_SECRET="$(pwgen 32 1)"
export DB_PASSWORD="$(pwgen 32 1)"
export MINIO_ACCESS_KEY="$(pwgen 32 1)"
export MINIO_SECRET_KEY="$(pwgen 32 1)"
kubectl create secret generic auth-secrets --namespace magda --from-literal=jwt-secret=$JWT_SECRET --from-literal=session-secret=$SESSION_SECRET
kubectl --namespace magda annotate --overwrite secret auth-secrets replicator.v1.mittwald.de/replication-allowed=true replicator.v1.mittwald.de/replication-allowed-namespaces=magda-openfaas-fn
kubectl create secret generic db-passwords --namespace magda \
--from-literal=combined-db=$DB_PASSWORD \
--from-literal=authorization-db=$DB_PASSWORD \
--from-literal=content-db=$DB_PASSWORD \
--from-literal=session-db=$DB_PASSWORD \
--from-literal=registry-db=$DB_PASSWORD \
--from-literal=combined-db-client=$DB_PASSWORD \
--from-literal=authorization-db-client=$DB_PASSWORD \
--from-literal=content-db-client=$DB_PASSWORD \
--from-literal=session-db-client=$DB_PASSWORD \
--from-literal=registry-db-client=$DB_PASSWORD \
--from-literal=tenant-db=$DB_PASSWORD \
--from-literal=tenant-db-client=$DB_PASSWORD
kubectl create secret generic storage-secrets --namespace magda --from-literal=accesskey=$MINIO_ACCESS_KEY --from-literal=secretkey=$MINIO_SECRET_KEY
# Optional; Only for sending email notification of user inquires
kubectl create secret generic smtp-secret --namespace magda --from-literal=username=$SMTP_USERNAME --from-literal=password=$SMTP_PASSWORD
8> Install Magda via Helm
helm upgrade --namespace magda --install --timeout 9999s --set magda-core.gateway.service.type=LoadBalancer magda oci://ghcr.io/magda-io/charts/magda
Since v2, we release our helm charts to Github container registry:
oci://ghcr.io/magda-io/charts
By default, Helm will install the latest production version of Magda. You can use
--versionto specify the exact chart version to use. e.g.:
helm upgrade --namespace magda --install --version 0.0.60-rc.1 --timeout 9999s --set magda-core.gateway.service.type=LoadBalancer magda oci://ghcr.io/magda-io/charts/magda
The value --set magda-core.gateway.service.type=LoadBalancer will expose Magda via load balancer.
You can run:
echo $(kubectl get svc --namespace magda gateway --template "")
to find out the load balancer external IP. And access Magda via http://[External IP].
To expose Magda via Ingress and Setup TLS / SSL, you can follow this docs